Precision machining is a highly specialized manufacturing process designed to produce components with tight tolerances, intricate designs, and excellent surface finishes. The process involves the removal of material from a workpiece using advanced tools and machines, including:
Key Processes: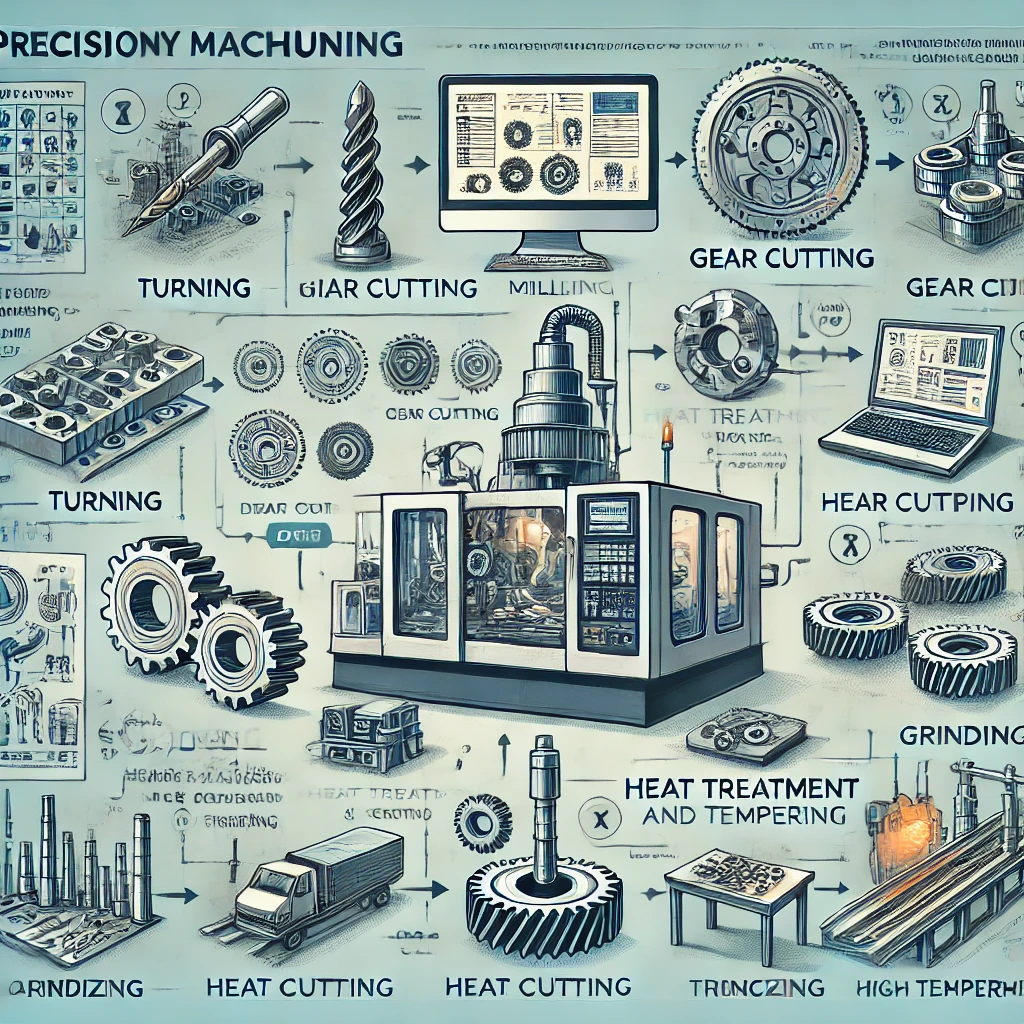
- Turning: Rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material, shaping it into cylindrical or conical forms.
- Milling: Using rotary cutters to remove material from the workpiece, creating precise shapes, slots, or contours.
- Drilling: Creating holes with high accuracy using drill bits.
- Gear Cutting: Producing gears with precise dimensions and profiles.
- Honing: Enhancing surface finish and dimensional accuracy of bores or cylindrical components.
- Grinding: Achieving fine surface finishes and precise dimensions by using abrasive tools.
Heat Treatment:
Special processes like carburizing, quenching, and tempering are often integrated into precision machining to enhance material properties such as hardness, strength, and wear resistance.
CNC Programming:
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems are used to automate machining processes, enabling the production of complex components by following detailed digital designs. CNC allows multi-axis operations, ensuring precision in multiple dimensions.
Applications:
Precision-machined parts are critical for industries such as:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Medical Devices
- Electronics
- Energy
This process ensures the production of components that meet exacting standards for OEMs and system integrators, serving diverse end-markets with unparalleled quality and reliability. Let me know if you need a detailed write-up or visualizations!
